Church of San Martín
San Martín de Tours is a church in Frómista, province of Palencia, Spain. Built in the 11th century in Romanesque style, it is located across theWay of Santiago.
The church was begun in the second half of the 11th century by will of queen Mayor of Castile, as part of a monastery, which has disappeared. The church is mentioned for the first time in 1066, and is stylistically connected to other Romanesque edifices in the province, such as the Cathedral of Jaca.
In 1118 it was assigned to the Benedictine priory of San Zoilo at Carrión de los Condes. The monks abandoned the site in the 13th century, giving it to Don Juan Gómez de Manzanedo. During several changes of ownership in the following centuries, the church received several in the 15th century: a bell tower over the original dome, and other units which acted as sacristy. After the Middle Ages it started to decay, and in the 19th century it was declared no more fit for celebrations.
In 1894 it was declared a National Monument and a restoration was started. This brought the church back to its original state, removing numerous later additions. The church was reopened to the public in 1904.
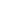
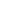
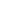
St. Martin has a typical Romanesque exterior. The three-level façade shows the difference height of the nave and aisles of the interior; at the sides are two cylindrical bell towers, while, in correspondence of the crossing, is an octagonal dome. The nave and the aisle, covered with barrel vaults, end with three apses.
The church has four entrances, one for each of its sides. However, only two are currently opened. The walls have a solid appearance, with few windows enclosed in rounded arches. All the four sides are topped by some 300 modillions with human, animals and fantastic figures, including some erotic scenes.Above the main portal is achrismon with six arms.
The interior is on the basilica plan, with four bays separated by piers. The apses have several medieval sculptures, including a 13th century Christ in the nave. Some of the capitals have motifs of vegetables, human figures or depictions of stories, such as that of Adam and Eve or the Fox and the Grape.